Yes, solar panel installation is worth it for many U.S. homeowners in 2026. Homes with high electricity bills, good roof conditions, and long-term ownership see the strongest returns. Federal tax credits, rising utility rates, and long system lifespans make solar a valuable investment in many states.
Solar panel installation is growing fast across the United States of America. Rising electricity rates push many homeowners toward solar energy. However, solar does not suit every American household due to some crucial reasons, such as roof top condition, sunlight hitting, location, etc.
This guide explains costs, savings, and payback clearly for U.S. homes. Most homeowners want clarity before reviewing detailed information. Here is a straightforward answer based on U.S. market data. Solar adoption continues to grow among U.S. homeowners facing rising utility costs.
Is Solar Panel Installation Worth It in the USA in 2026?
Yes, solar installation is worth it for many U.S. homeowners. Homes with higher electricity usage gain the most value. Federal tax credits significantly lower the upfront costs of solar installation. Long-term savings often exceed total system expenses. Many homeowners offset a large portion of their monthly electricity bills with solar systems.
When Solar Panel Installation Is NOT Worth It in the USA
Solar is not ideal for every homeowner. Roofs with heavy shading reduce solar energy production. Homeowners planning to move soon may not be able to recover their costs. Very low electric bills limit overall solar savings. Homes with bills under modest monthly levels often see slower returns.
Solar Panel Installation Cost in the USA
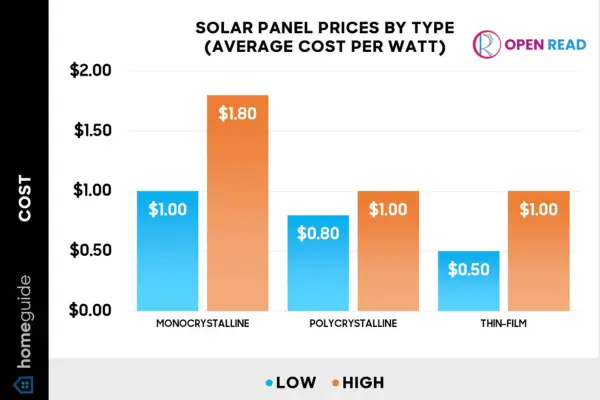
Solar installation costs vary by location and system size. Prices declined steadily across the U.S. market. Still, solar remains a major financial commitment for homeowners. Local utility rules and labor costs also affect final pricing. A mid-size system serves the average U.S. household efficiently.
Average Solar Installation Cost in the United States
In 2026, the average residential solar panel installation in the USA costs between $15,000 and $25,000 before incentives. After applying the federal solar tax credit, many homeowners pay significantly less out of pocket. Final cost depends on system size, roof type, and local labor rates.
Cost per watt in the USA
Most U.S. homeowners pay approximately $2.50 to $3.50 per watt for residential solar installation in 2026. Larger systems generally cost less per watt, while smaller systems tend to have higher per-watt pricing.
Solar system installation size for U.S. homes
Most American homes install systems between 6 kW and 8 kW. This capacity of the solar system is suitable for the average U.S. household and covers a large portion of annual electricity usage. In 2026, a 6 kW to 8 kW residential solar system in the USA typically costs between $15,000 and $25,000 before incentives, depending on location and roof complexity. For a detailed breakdown of installation costs by state and system size, see our complete guide on solar panel installation in the USA.
Solar Cost Breakdown for American Homeowners
Understanding cost categories prevents unexpected expenses. Each system component affects the total installation price. You can explore a full cost breakdown, including labor and permit fees, in our residential solar installation cost guide.
Solar panels & inverter cost
Solar panels represent the largest share of total costs. Inverters convert solar power into usable household electricity. The solar panel and inverter cost varies depending on the brand, capacity, etc.
Installation, labor & permits
Labor costs vary widely across U.S. states. Local permits and inspections increase installation expenses.
Grid connection & inspection fees
Utility companies charge fees for grid interconnection. Final inspections ensure safety and regulatory compliance.
State-by-State Solar Cost & Savings in the USA
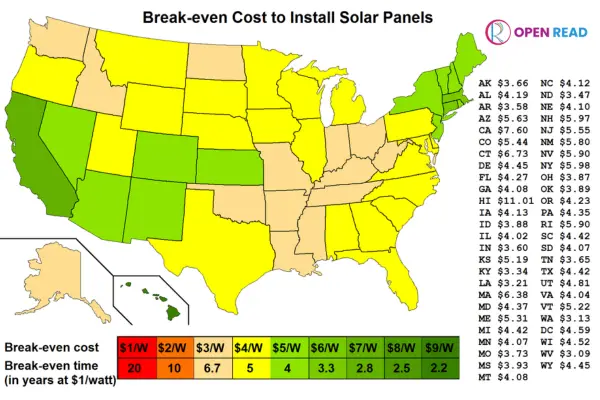
Solar value changes widely across different U.S. states. Electricity rates, sunlight, and incentives drive these differences. State policies strongly influence solar profitability. States with higher electricity rates usually deliver faster solar payback periods. It is noted that States with high electricity rates and strong incentives often see faster solar returns. Solar savings depend heavily on your state. You can explore detailed cost and savings guides below:
- Solar panel installation cost in Arizona
- Solar system installation in California
- In Florida solar panel installation cost
- Solar panel installation cost in New York
- Solar panel installation cost in Texas
Best States in the USA for Solar Panel Installation
Some states offer exceptional solar benefits. In high-cost electricity states, homeowners often save between $1,200 and $2,500 per year on electricity after installing solar. Payback periods in these states can be significantly shorter due to higher utility rates and strong incentive programs.
States Where Solar Is Less Profitable
Not all states offer strong solar returns. In states with low electricity rates, annual solar savings are usually smaller. Homeowners may see longer payback periods, especially if incentives are limited or net metering policies are weak.
Why Solar ROI Changes by State in the USA
Electric utility rates vary by state. Sun exposure differs across geographic regions. Local incentives impact upfront installation costs. Net metering rules affect long-term savings.
Federal & State Solar Incentives in the USA
Incentives make solar more affordable for American homeowners. Federal and state programs reduce total installation costs. Understanding incentives improves financial decisions.
Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The federal government offers a solar tax credit. It applies to residential solar installations nationwide. Federal incentives remain one of the strongest drivers of residential solar adoption.
How much can Americans claim
Eligible homeowners can claim a percentage of system costs. The credit reduces federal income tax liability directly.
Who Qualifies for The Tax Credit?
Homeowners must own the solar system. The system must be installed on a primary residence. Tax liability is required to use the credit.
State Solar Rebates & Net Metering Policies
Many states provide additional solar rebates. Net metering credits the excess energy sent to the grid. Policies vary significantly between states.
How Much Money Can Solar Panels Save in the USA?
Solar panels reduce long-term electricity expenses. Savings depend on usage, system size, and location. Most homeowners see steady bill reductions. Solar also protects homeowners from long-term electricity price increases.
Average U.S. Electricity Bill vs Solar Savings
The average U.S. electricity bill continues rising. Solar offsets a large portion of monthly energy costs. Higher usage increases potential savings.
10-Year and 25-Year Savings Projection
Solar systems operate efficiently for decades. Long-term savings often exceed the initial investment. Maintenance costs remain relatively low.
Solar Payback Period for U.S. Homeowners
Solar payback periods in the USA typically range from 6 to 12 years, depending on state electricity rates, system size, and available incentives. Homes in high-rate states often reach breakeven faster, while low-rate states may take longer.
Example: Solar Payback for a U.S. Home
A homeowner with a $180 monthly electric bill installs a 7 kW solar system. After the federal tax credit, the system cost drops significantly. Monthly electric bills fall sharply, and the system pays for itself within several years, depending on state incentives and utility rates.
Is Solar Worth It for Your Home Type in the USA?
Solar value depends heavily on home type. Roof structure, ownership, and usage patterns matter greatly. Not every U.S. home benefits equally from solar panels. Roof ownership and energy usage strongly influence solar outcomes. Roof type and condition play a major role in solar performance. Learn more in our rooftop solar panel installation guide for U.S. homes.
Single-Family Homes
Single-family homes are ideal for solar installation. Small family homes typically see the highest solar savings in the USA due to full roof control, higher energy usage, and easier system sizing. Higher energy usage increases long-term savings.
Townhomes & HOA-Restricted Properties
Townhomes face additional solar restrictions. Homeowners Association (HOA) approval is often required before installation. Solar savings for townhomes vary widely and depend on HOA approval, available roof space, and shared ownership rules.
Mobile & Manufactured Homes
Mobile homes can support solar systems. Permanent foundation installation is usually required. Roof strength must meet panel weight standards. Solar can be cost-effective for mobile homes, but ground-mounted systems are sometimes a better option.
Rural vs Urban Homes in the USA
Rural homes often have more installation space. Fewer shading issues improve solar output. Urban homes face roof limitations and zoning rules. Rural homes often achieve faster solar payback due to fewer shading issues, while urban homes depend more on roof orientation and local electricity rates.
Solar Panel Performance in Different U.S. Climates
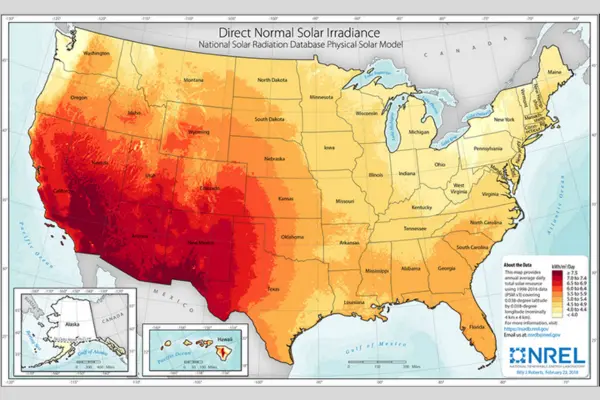
Solar panels perform differently across U.S. climates. Weather conditions affect annual energy production. Modern systems handle temperature changes efficiently.
Hot Climate States (Texas, Arizona, Florida)
Solar panels perform well in sunny states. High sunlight increases energy production. Extreme heat slightly reduces panel efficiency. Across all U.S. climates, modern solar panels remain effective, but total annual savings depend on sunlight levels, electricity rates, and net metering policies.
Cold & Snowy States
Solar panels work in cold climates. Snow usually slides off tilted panels. Cold temperatures improve electrical efficiency. Winter sunlight still generates usable power.
Cloudy & Low-Sun Regions
Solar panels produce energy on cloudy days. Output decreases but does not stop completely. Net metering helps offset lower production. Annual savings remain possible in these regions.
Are Solar Financing Options Available in the USA?
Yes, financing determines overall solar affordability. Different payment options suit different homeowners. Understanding terms prevents long-term regret.
Cash Purchase Vs Solar Loan
Cash purchases offer the highest lifetime savings. Loans reduce upfront costs for homeowners. Loan interest affects the total system cost. Ownership allows full access to tax credits.
| Factor | Cash Purchase | Solar Loan |
| Upfront Cost | High initial payment | Low or moderate upfront cost |
| System Ownership | The homeowner owns the system | Monthly loan payments are required |
| Federal Tax Credit | 100% eligible | 100% eligible |
| Monthly Payments | No monthly payments | Homeowners avoiding high upfront costs |
| Total Lifetime Cost | Lowest overall cost | Higher due to interest |
| Long-Term Savings | Maximum savings | Reduced savings |
| Credit Score Impact | Not required | Credit score required |
| Home Resale Impact | Simple home resale | Loan transfer may be required |
| Best For | Homeowners with savings | Homeowners avoiding large upfront costs |
Many homeowners choose loans to avoid large upfront payments.
Solar Lease & Power Purchase Agreement (PPA)
Leases and PPAs require little upfront payment. Monthly payments replace utility bills partially. System ownership stays with the provider. Lease terms often favor providers more than homeowners.
Why leases are risky for U.S. homeowners
Leases limit tax credit eligibility. Selling homes becomes more complicated. Long contracts reduce financial flexibility.
- Homeowners do not own the solar system.
- Federal solar tax credits usually go to the provider.
- Long contracts limit financial flexibility.
- Selling a home becomes more complicated.
- Buyers may refuse to assume lease agreements.
- Monthly payments can increase over time.
- Early termination fees are often expensive.
Solar Panels and Home Value in the USA
Solar panels can affect home value positively. Impact depends on ownership, location, and buyer perception. Most U.S. buyers prefer homes with lower energy costs.
Do Solar Panels Increase Property Value?
Yes, solar panels often increase home value. Buyers value lower monthly electricity bills. Owned systems add more value than leased systems. Appraisers may consider solar during valuation.
Selling a Home with Solar Panels in America
Homes with solar often sell faster. Energy savings attract budget-conscious buyers. Owned systems simplify the selling process. Leased systems may require buyer approval.
Owned vs Leased Systems: Which Is Better?
Owned systems provide full financial benefits. Leased systems offer limited resale flexibility. Buyers prefer clear ownership without contracts. Ownership improves long-term property value.
| Factor | Owned Solar System | Leased Solar System |
| System Ownership | Homeowner owns the system | Solar company owns the system |
| Upfront Cost | Higher initial cost | Little or no upfront cost |
| Federal Tax Credit | Homeowner claims the credit | Provider claims the credit |
| Monthly Payments | No monthly payment | Monthly lease payment |
| Long-Term Savings | Highest lifetime savings | Lower overall savings |
| Home Resale Impact | Easy home resale | Can complicate home selling |
| Contract Length | No long-term contract | Long-term lease agreement |
| Maintenance Responsibility | Usually homeowner | Usually provider |
| Best For | Long-term homeowners | Short-term budget-focused users |
Common U.S. Homeowner Concerns About Solar
Many homeowners share similar solar concerns. Understanding risks helps reduce hesitation. Most concerns have practical solutions.
What If I Move After Installing Solar?
Moving early may limit financial returns. Owned systems transfer easily during resale. Leases complicate buyer negotiations. Longer ownership improves solar value recovery.
Roof Damage, Maintenance & Warranty Issues
Solar panels do not damage healthy roofs. Installers seal mounts to prevent leaks. Panels require minimal ongoing maintenance. Warranties often last twenty years or more.
Are Solar Panels Reliable in the USA?
Modern solar panels are highly reliable. Systems withstand rain, wind, and snow. Performance degradation happens slowly. Most panels operate efficiently for decades.
Final Verdict: Should You Install Solar Panels in the USA?
Yes, solar panel installation is worth it for many U.S. homeowners in 2026. Homes with high electricity bills, good roof conditions, and long-term ownership see the strongest financial returns. Rising utility costs and federal tax incentives continue to improve solar value. Solar may not be ideal for short-term homeowners, heavily shaded roofs, or homes with very low electricity usage. In these cases, savings take longer to recover. The best results come from careful planning, realistic cost analysis, and comparing multiple solar installers. When installed correctly, solar panels offer long-term savings, energy stability, and increased home value for American homeowners.
FAQs: Should You Install Solar Panels in the USA?
Who Should Install Solar Panels Now?
U.S. homeowners with high electricity bills benefit the most from solar. Those planning to stay in their home long-term and having good sunlight exposure usually see the strongest returns.
Who Should Wait Before Installing Solar?
Short-term homeowners may want to wait. Homes with heavy roof shading or very low electricity usage often see slower payback.
How Can I Get an Accurate Solar Quote in the USA?
Request quotes from at least three licensed solar installers. Compare pricing, warranties, financing options, and local incentives before deciding. Before choosing a provider, review our guide on the best residential solar panel installation companies in the USA.
Is Solar Worth It for the Average U.S. Homeowner?
Yes, solar is worth it for many U.S. homeowners when electricity costs are high, and incentives apply. Savings depend on roof condition, location, and energy usage.

Rajib Hasan is a U.S.-focused solar energy analyst and residential & commercial solar PV consultant with over 8 years of experience in rooftop system design, solar installation cost analysis, AHJ permitting processes, NEC compliance, and net energy metering (NEM). He works closely with American homeowners and businesses to evaluate solar installers, navigate federal and state incentive programs, and make data-driven, long-term solar investment decisions.
Expertise Areas:
- S. residential & commercial solar installation costs
- AHJ permitting & utility interconnection processes
- NEC (National Electrical Code) compliance
- Net Energy Metering (NEM 2.0 & NEM 3.0)
- Federal solar tax credits (IRS Sections 25D & 48)

